
Aircraft engines power a wide range of planes, from small private aircraft to massive commercial jets. Each type of aircraft engine: piston, turboprop, and turbofan has distinct features tailored to specific aviation needs. In general aviation, piston aircraft engines are preferred for their affordability and ease of maintenance. TurboProp engines combine the reliability of piston engines with turbine efficiency, making them popular in regional flights. TurboFan engines provide the high thrust needed for larger and faster commercial and military aircraft.
Choosing the right type of aircraft engine depends on factors like thrust-to-weight ratio, engine weight, and fuel efficiency, all of which impact long-term operating costs and environmental considerations.
Read More: How to Choose The Best Flight School For You?
Piston aircraft engines are among the oldest and most commonly used for light aircraft. These engines power propeller-driven planes by burning fuel to move pistons, which then rotate the propeller. Known for their simplicity, piston engines are reliable and economical.
Advantages of Piston Aircraft Engines:
Lower Operating Costs: Piston engines require minimal maintenance compared to more complex turbine engines.
Fuel Efficiency: Piston engines are efficient for short, low-altitude flights, making them ideal for general aviation.
Environmental Considerations: Emissions are typically lower at lower altitudes, making piston engines a more sustainable choice for certain flights.
Applications: Piston aircraft engines are commonly used in training aircraft, private planes, and other general aviation settings for short trips and lower-speed operations.
TurboProp engines blend the power of turbine engines with a propeller, making them suitable for regional aviation. TurboProp engines drive the propeller using a turbine and jet fuel, which increases efficiency at medium altitudes.
Advantages of TurboProp Aircraft Engines:
Fuel Efficiency: TurboProps excel in fuel efficiency compared to TurboFan engines, particularly at lower speeds and altitudes.
Versatility: TurboProps offer a balanced combination of speed and range, which is perfect for regional flights.
Performance: While still utilizing a propeller, TurboProps generate more power than piston engines, enabling higher speeds and payloads.
Applications: Aircraft like the Bombardier Dash 8 and ATR 72 rely on TurboProp engines for regional and cargo flights, given their balanced performance and efficiency.
TurboFan engines, primarily jet engines, power the commercial aviation sector. These engines operate by compressing and igniting air to produce thrust, propelling aircraft at high speeds. Despite being heavier, TurboFan engines offer a superior thrust-to-weight ratio, which is vital for high-speed and long-distance travel.
Advantages of TurboFan Aircraft Engines:
High Thrust to Weight Ratio: TurboFan engines provide a much higher thrust relative to their weight than other types of aircraft engines.
Superior Fuel Efficiency at Cruise Altitudes: TurboFan are highly fuel-efficient at high altitudes, making them ideal for long-haul flights.
Environmental Impact: Although emissions are higher during takeoff, turbine engines’ efficiency at cruising altitude mitigates their environmental footprint over long distances.
Applications: TurboFan engines are widely used in commercial jets like the Boeing 737 and Airbus A320 for their capacity to cover long distances with higher passenger and cargo loads.
Read More: What Are Flight Control Surfaces?
When choosing aircraft engines, factors like performance, cost, and environmental impact are key considerations. Below is a quick comparison:
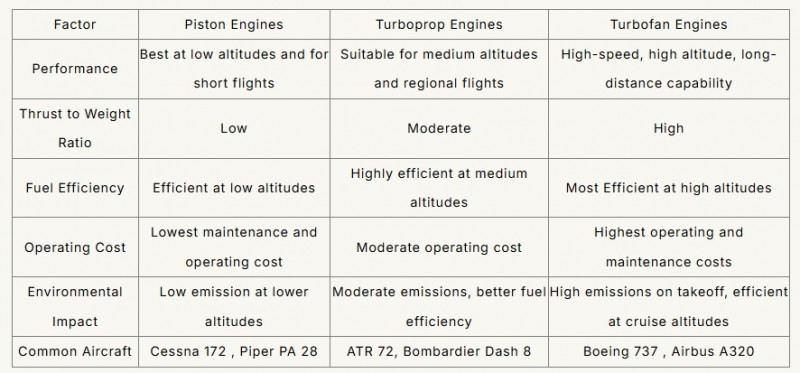
Aircraft Engines Comparison (Source Picture: 14DAYPILOT)
In aviation, the debate over piston vs. turboprop vs. turbofan aircraft engines highlights the unique benefits each offers for different applications. Your choice depends on factors such as flight range, operational costs, and environmental goals. Continuous advancements in aircraft engine technology promise improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and innovations that will shape the future of aviation.
By understanding each engine type, pilots and aviation enthusiasts can make informed choices that align with their specific needs and priorities. If you're eager to deepen your understanding of aircraft engines and enhance your flying skills, consider joining our 14 Day Accelerated Private Pilot Program. At 14daypilot, the world’s leading accelerated flight school, you’ll gain valuable insights while enjoying a dynamic learning experience.

Aircraft engines play a crucial role in the world of aviation, helping pilots and enthusiasts make informed decisions. Whether you're piloting a single-prop aircraft or a commercial airliner, understanding the benefits and drawbacks of each engine type: piston, turboprop, and TurboFan is essential. In this article, we’ll compare these engines in terms of performance, fuel efficiency, operating costs, and applications, providing a comprehensive look at the factors that drive engine choice in aviation.
Aircraft engines power a wide range of planes, from small private aircraft to massive commercial jets. Each type of aircraft engine: piston, turboprop, and turbofan has distinct features tailored to specific aviation needs. In general aviation, piston aircraft engines are preferred for their affordability and ease of maintenance. TurboProp engines combine the reliability of piston engines with turbine efficiency, making them popular in regional flights. TurboFan engines provide the high thrust needed for larger and faster commercial and military aircraft.
Choosing the right type of aircraft engine depends on factors like thrust-to-weight ratio, engine weight, and fuel efficiency, all of which impact long-term operating costs and environmental considerations.
Read More: How to Choose The Best Flight School For You?
Piston aircraft engines are among the oldest and most commonly used for light aircraft. These engines power propeller-driven planes by burning fuel to move pistons, which then rotate the propeller. Known for their simplicity, piston engines are reliable and economical.
Advantages of Piston Aircraft Engines:
Lower Operating Costs: Piston engines require minimal maintenance compared to more complex turbine engines.
Fuel Efficiency: Piston engines are efficient for short, low-altitude flights, making them ideal for general aviation.
Environmental Considerations: Emissions are typically lower at lower altitudes, making piston engines a more sustainable choice for certain flights.
Applications: Piston aircraft engines are commonly used in training aircraft, private planes, and other general aviation settings for short trips and lower-speed operations.
TurboProp engines blend the power of turbine engines with a propeller, making them suitable for regional aviation. TurboProp engines drive the propeller using a turbine and jet fuel, which increases efficiency at medium altitudes.
Advantages of TurboProp Aircraft Engines:
Fuel Efficiency: TurboProps excel in fuel efficiency compared to TurboFan engines, particularly at lower speeds and altitudes.
Versatility: TurboProps offer a balanced combination of speed and range, which is perfect for regional flights.
Performance: While still utilizing a propeller, TurboProps generate more power than piston engines, enabling higher speeds and payloads.
Applications: Aircraft like the Bombardier Dash 8 and ATR 72 rely on TurboProp engines for regional and cargo flights, given their balanced performance and efficiency.
TurboFan engines, primarily jet engines, power the commercial aviation sector. These engines operate by compressing and igniting air to produce thrust, propelling aircraft at high speeds. Despite being heavier, TurboFan engines offer a superior thrust-to-weight ratio, which is vital for high-speed and long-distance travel.
Advantages of TurboFan Aircraft Engines:
High Thrust to Weight Ratio: TurboFan engines provide a much higher thrust relative to their weight than other types of aircraft engines.
Superior Fuel Efficiency at Cruise Altitudes: TurboFan are highly fuel-efficient at high altitudes, making them ideal for long-haul flights.
Environmental Impact: Although emissions are higher during takeoff, turbine engines’ efficiency at cruising altitude mitigates their environmental footprint over long distances.
Applications: TurboFan engines are widely used in commercial jets like the Boeing 737 and Airbus A320 for their capacity to cover long distances with higher passenger and cargo loads.
Read More: What Are Flight Control Surfaces?
When choosing aircraft engines, factors like performance, cost, and environmental impact are key considerations. Below is a quick comparison:

Aircraft Engines Comparison (Source Picture: 14DAYPILOT)
In aviation, the debate over piston vs. turboprop vs. turbofan aircraft engines highlights the unique benefits each offers for different applications. Your choice depends on factors such as flight range, operational costs, and environmental goals. Continuous advancements in aircraft engine technology promise improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and innovations that will shape the future of aviation.
By understanding each engine type, pilots and aviation enthusiasts can make informed choices that align with their specific needs and priorities. If you're eager to deepen your understanding of aircraft engines and enhance your flying skills, consider joining our 14 Day Accelerated Private Pilot Program. At 14daypilot, the world’s leading accelerated flight school, you’ll gain valuable insights while enjoying a dynamic learning experience.
Ilham Febrian is a dedicated aviation blogger with a strong interest and high expectations for the aviation industry. He holds a DGCA Commercial Pilot license with Airbus A320 type rating. Continuously updated with the latest aviation news, Ilham strives to provide top-quality content on the website, aimed at assisting all pilots. The website focuses on offering flight training guidance, information on flying school materials, and tips on how students can successfully pass their check rides.
Ilham Febrian is a dedicated aviation blogger with a strong interest and high expectations for the aviation industry. He holds a DGCA Commercial Pilot license with Airbus A320 type rating. Continuously updated with the latest aviation news, Ilham strives to provide top-quality content on the website, aimed at assisting all pilots. The website focuses on offering flight training guidance, information on flying school materials, and tips on how students can successfully pass their check rides.